User registration
This database reflects the set of users of water resources and guides some of the main management instruments, such as grants and charges. In addition to these, other instruments, such as the classification of water bodies and the Basin Plan, have in the register an important source of information.
According to the State Water Resources Policy (State Law No. 3.329 / 99 [PFA1]), individuals or legal entities governed by public or private law that collect or consume water, release effluents or carry out non-consumptive uses are classified as water users directly in water bodies, such as rivers, streams, lakes or aquifers, in the State of Rio de Janeiro.
Registration is a prerequisite for requesting a permit for the use of water and environmental certificates of water reserve and insignificant use in the State, in addition to serving as a basis for charging for the use of water.
Currently, the State Institute for the Environment (INEA) is responsible for managing the register of users of water resources under state ownership. Users are responsible for carrying out the registration, which is self-declaratory.
On October 17, 2006, through State Decree No. 40.156, [PFA2] the State of Rio de Janeiro institutionalized the National Register of Water Resources Users (CNARH) as the only register in the State for the state of domain waters, Facilitate and expand the process of regularizing the use of water.
After ten years of integrating the registries of water users at the federal and state levels, a new stage begins with the technological evolution of the registration and management system for registries prepared and developed by the National Water Agency (ANA).
The new CNARH, CNARH 40, aimed at users who want to become regularized, changed the concept of registration. The previous one, CNARH 1.0, adopted the concept of integrated enterprise, and registered under the same registration number (declaration) all interferences (captures and releases into water bodies) and all uses/purposes of the enterprise. The CNARH 40, on the other hand, adopts peer-to-peer registration. This means that each interference point will be processed with a corresponding usage and throughput impact.
The water resources user registration platform was also redesigned. The Federal Use Regulation System (REGLA) can be accessed at www.snirh.gov.br/cnarh.
CNARH 40 only considers regularized registries, that is, interference points that have an insignificant use license or certificate, or that are in the process of analysis. Thus, from the year 2018 onwards, the information from the registries of the Guandu Hydrographic Region will only present those from regularized interference points or in the process of regularization.
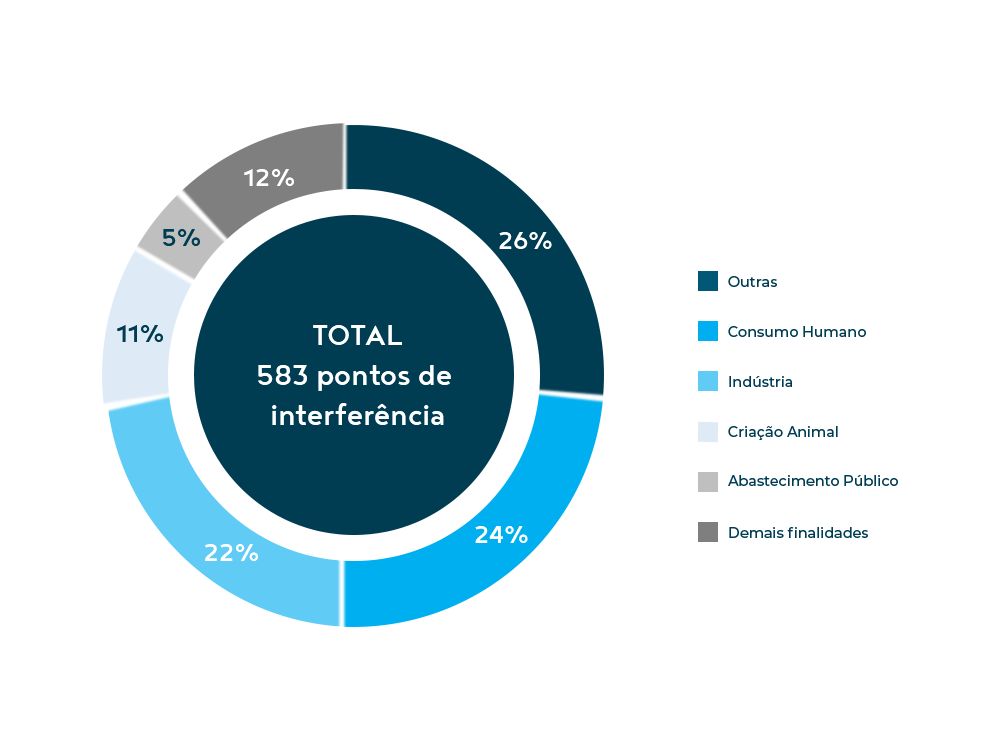
Currently, 583 interference points (there were 475 at the end of 2019) are registered in the Guandu Hydrographic Region, divided between Captures and Launches, as shown in the table below.
Pontos de interferência por finalidade de uso
Click here for more information on CNARH 40 and REGLA.
